What is an Earthing or Grounding?
The process of connecting the metallic frame (i.e. non-current carrying part) of electrical equip-ment or some electrical part of the system (e.g. neutral point in a star-connected system, one conductor of the secondary of a transformer etc.) to earth (i.e. soil) is called grounding or earthing.
It is strange but true that grounding of electrical systems is less understood aspect of power system. Nevertheless, it is a very important subject. If grounding is done systematically in the line of the power system, we can effectively prevent accidents and damage to the equipment of the power
system and at the same time continuity of supply can be maintained. Grounding or earthing may be
classified as :
(i) Equipment grounding
(ii) System grounding.
Equipment grounding deals with earthing the non-current-carrying metal parts of the electrical
equipment. On the other hand, system grounding means earthing some part of the electrical system
e.g. earthing of neutral point of star-connected system in generating stations and sub-stations.
First, it provides protection to the power system. For example, if the neutral point of a star-connected system is grounded through a circuit breaker and phase to earth fault occurs on any one line, a large fault current will flow through the circuit breaker. The circuit breaker will open to isolate the faulty line. This protects the power system from the harmful
effects of the fault. Secondly, earthing of electrical equipment (e.g. domestic appliances, hand-held tools, industrial motors etc.) ensures the safety of the persons handling the equipment.
Types of earthing or grounding ;
(i) Equipment grounding:-
The process of connecting non-current-carrying metal parts (i.e. metallic enclosure) of the electri cal equipment to earth (i.e. soil) in such a way that in case of insulation failure, the enclosure effectively remains at earth potential is called equipment grounding.
(ii) System grounding:-
The process of connecting some electrical part of the power system (e.g. neutral point of a star- connected system, one conductor of the secondary of a transformer etc.) to earth (i.e.
soil) is called system grounding.
Neutral Grounding:-
The process of connecting neutral point of 3-phase system to earth (i.e. soil) either directly or through some circuit element (e.g. resistance, reactance etc.) is called neutral grounding.
Advantages of Neutral Grounding
The following are the advantages of neutral grounding :
(i) Voltages of the healthy phases do not exceed line to ground voltages i.e. they remain nearly constant.
(ii) The high voltages due to arcing grounds are eliminated.
(iii) The protective relays can be used to provide protection against earth faults. In case earth fault occurs on any line, the protective relay will operate to isolate the faulty line.
(iv) The overvoltages due to lightning are
discharged to earth.
(v) It provides greater safety to personnel and equipment.
(vi) It provides improved service reliability.
(vii) Operating and maintenance expenditures are reduced.
Methods of Neutral Grounding
The methods commonly used for grounding the neutral point of a 3-phase system are :
(i) Solid or effective grounding
(ii) Resistance grounding
(iii) Reactance grounding
The choice of the method of grounding depends upon many factors including the size of the system, system voltage and the scheme of protection to be used.
When the neutral point of a 3-phase system (e.g. 3- phase generator, 3-phase transformer etc.) is directly *connected to earth (i.e. soil) through a wire of negligible resistance and reactance, it is called solid grounding or effective grounding.
When the neutral point of a 3-phase system (e.g. 3-phase generator, 3-phase transformer etc.) is connected to earth (i.e. soil) through a resistor, it is called resistance grounding.
Or
In order to limit the magnitude of earth fault current, it is a common practice to connect the neutral point of a 3-phase system to earth through a resistor. This is called resistance grounding.
The process of connecting the metallic frame (i.e. non-current carrying part) of electrical equip-ment or some electrical part of the system (e.g. neutral point in a star-connected system, one conductor of the secondary of a transformer etc.) to earth (i.e. soil) is called grounding or earthing.
It is strange but true that grounding of electrical systems is less understood aspect of power system. Nevertheless, it is a very important subject. If grounding is done systematically in the line of the power system, we can effectively prevent accidents and damage to the equipment of the power
system and at the same time continuity of supply can be maintained. Grounding or earthing may be
classified as :
(i) Equipment grounding
(ii) System grounding.
Equipment grounding deals with earthing the non-current-carrying metal parts of the electrical
equipment. On the other hand, system grounding means earthing some part of the electrical system
e.g. earthing of neutral point of star-connected system in generating stations and sub-stations.
First, it provides protection to the power system. For example, if the neutral point of a star-connected system is grounded through a circuit breaker and phase to earth fault occurs on any one line, a large fault current will flow through the circuit breaker. The circuit breaker will open to isolate the faulty line. This protects the power system from the harmful
effects of the fault. Secondly, earthing of electrical equipment (e.g. domestic appliances, hand-held tools, industrial motors etc.) ensures the safety of the persons handling the equipment.
Types of earthing or grounding ;
(i) Equipment grounding:-
The process of connecting non-current-carrying metal parts (i.e. metallic enclosure) of the electri cal equipment to earth (i.e. soil) in such a way that in case of insulation failure, the enclosure effectively remains at earth potential is called equipment grounding.
(ii) System grounding:-
The process of connecting some electrical part of the power system (e.g. neutral point of a star- connected system, one conductor of the secondary of a transformer etc.) to earth (i.e.
soil) is called system grounding.
Neutral Grounding:-
The process of connecting neutral point of 3-phase system to earth (i.e. soil) either directly or through some circuit element (e.g. resistance, reactance etc.) is called neutral grounding.
Advantages of Neutral Grounding
The following are the advantages of neutral grounding :
(i) Voltages of the healthy phases do not exceed line to ground voltages i.e. they remain nearly constant.
(ii) The high voltages due to arcing grounds are eliminated.
(iii) The protective relays can be used to provide protection against earth faults. In case earth fault occurs on any line, the protective relay will operate to isolate the faulty line.
(iv) The overvoltages due to lightning are
discharged to earth.
(v) It provides greater safety to personnel and equipment.
(vi) It provides improved service reliability.
(vii) Operating and maintenance expenditures are reduced.
Methods of Neutral Grounding
The methods commonly used for grounding the neutral point of a 3-phase system are :
(i) Solid or effective grounding
(ii) Resistance grounding
(iii) Reactance grounding
The choice of the method of grounding depends upon many factors including the size of the system, system voltage and the scheme of protection to be used.
- Solid grounding
When the neutral point of a 3-phase system (e.g. 3- phase generator, 3-phase transformer etc.) is directly *connected to earth (i.e. soil) through a wire of negligible resistance and reactance, it is called solid grounding or effective grounding.
- Resistance Grounding
When the neutral point of a 3-phase system (e.g. 3-phase generator, 3-phase transformer etc.) is connected to earth (i.e. soil) through a resistor, it is called resistance grounding.
Or
In order to limit the magnitude of earth fault current, it is a common practice to connect the neutral point of a 3-phase system to earth through a resistor. This is called resistance grounding.
- Reactance grounding
In this system, a reactance is inserted
between the neutral and ground The purpose of reactance is to limit the earth fault current. By changing
the earthing reactance, the earth fault current can to changed to obtain the conditions similar to that of solid grounding. This method is not used these days because of the following disadvantages :
(i) In this system, the fault current
required to operate the protec
tive device is higher than that of resistance grounding for the same fault conditions.
(ii) High transient voltages appear under fault conditions.










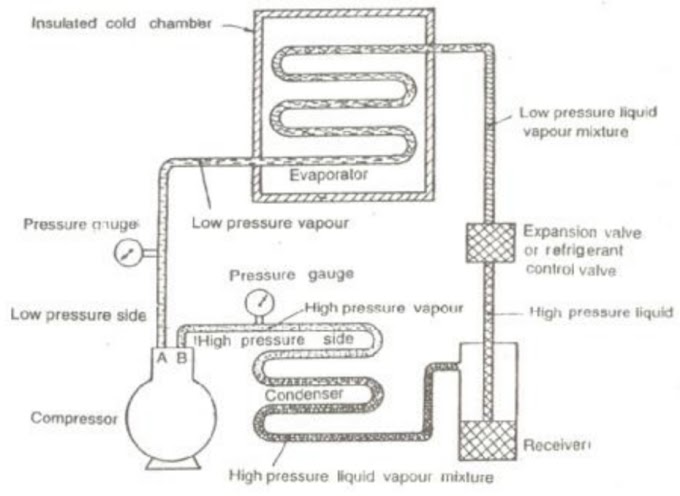








1 Comments
thanks
ReplyDelete