What is refrigeration?
VAPOUR COMPRESSION CYCLE
Vapour compression cycle is an improved type of air refrigeration cycle in which a
suitable working substance, termed as refrigerant, is used. The refrigerants generally used for this purpose are ammonia (NH3), carbon dioxide (CO2) and sulphur-dioxide (SO2). The refrigerant used, does not leave the system, but is circulated throughout the system alternately condensing and evaporating. In evaporating, the refrigerant absorbs its latent heat from the solution which is used for circulating it around the cold chamber and in condensing; it gives out its latent heat to the circulating water of the cooler.
The vapour compression cycle which is used in vapour compression refrigeration system
is now-a-days used for all purpose refrigeration. It is used for all industrial purposes from
a small domestic refrigerator to a big air conditioning plant.
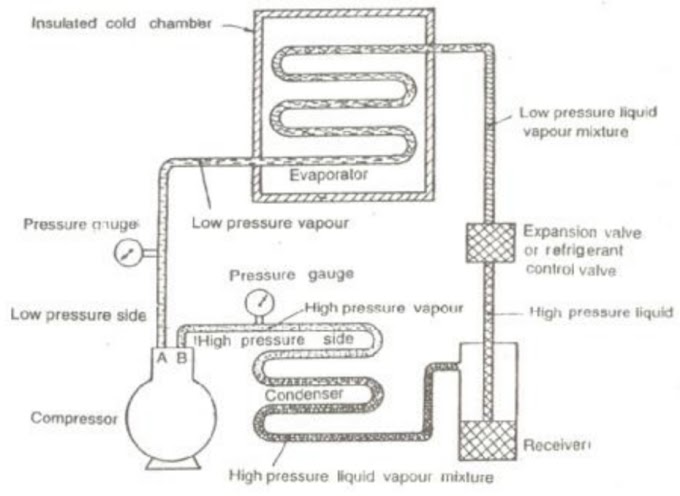
Simple Vapour Compression Refrigeration System
It consists of the following essential parts:
Compressor
The low pressure and temperature vapour refrigerant from evaporator is drawn into
the compressor through the inlet or suction valve A, where it is compressed to a
high pressure and temperature. This high pressure and temperature vapour refrigerant is discharged into the condenser through the delivery or discharge valve B.
Condenser
The condenser or cooler consists of coils of pipe in which the high pressure and temperature vapour refrigerant is cooled and condensed.The refrigerant, while passing through the condenser, gives up its latent heat to the
surrounding condensing medium which is normally air or water.
Receiver
The condensed liquid refrigerant from the condenser is stored in a vessel known as
receiver from where it is supplied to the evaporator through the expansion valve or
refrigerant control valve.
Expansion Valve
It is also called throttle valve or refrigerant control valve. The function of the
expansion valve is to allow the liquid refrigerant under high pressure and temperature to pass at a controlled rate after reducing its pressure and temperature.Some of the liquid refrigerant evaporates as it passes through the expansion valve, but the greater portion is vaporized in the evaporator at the low pressure and temperature .
Evaporator
An evaporator consists of coils of pipe in which the liquid-vapour. refrigerant at
low pressure and temperature is evaporated and changed into vapour refrigerant at
low pressure and temperature. In evaporating, the liquid vapour refrigerant absorbs
its latent heat of vaporization from the medium (air, water or brine) which is to be
cooled.











0 Comments