• Electric heating is a process in which electrical energy is converted to heat.
• When current is passed through a conductor, the conductor becomes hot (resistance heating).
• When a magnetic material is brought in the vicinity of an alternating magnetic field, heat
is produced in the magnetic material (induction heating).
• When an electrically insulating material was subjected to electrical stresses; it too underwent a temperature rise (dielectric heating).
• All heating requirements in domestic purposes such as cooking, room heater, immersion water heaters and electric toasters and also in industrial purposes such as welding, melting of metals, tempering, hardening, and drying can be met easily by electric heating over the other forms of conventional heating.
Advantages and disadvantages of electric heating
(a) Advantages
The various advantages of electric heating over other the types of heating are:
• Economical: Electric heating equipment is cheaper; they do not require much skilled
persons; therefore, maintenance cost is less.
• Cleanliness: Since dust and ash are completely eliminated in the electric heating, it keeps surroundings clean.
• Pollution free: As there are no flue gases in the electric heating, atmosphere around is pollution free; no need of providing space for their exit.
• Ease of control: In this heating, temperature can be controlled and regulated accurately either manually or automatically.
• Uniform heating: The substance can be heated uniformly throughout whether it may be conducting or non-conducting material.
• High efficiency: In non-electric heating, only 40-60% of heat is utilized but in electric heating 75-100% of heat can be successfully utilized. So, overall efficiency of electric heating is very high.
• Automatic protection: Protection against over current and overheating can be provided
by using control devices.
• Heating of non-conducting materials: The heat developed in the non-conducting materials such as wood and porcelain is possible only through the electric heating.
• Better working conditions: No irritating noise is produced with electric heating and also
radiating losses are low.
• Less floor area: Due to the compactness of electric furnace, floor area required is less.
• High temperature: High temperature can be obtained by the electric heating except the ability of the material to withstand the heat.
(b) Disadvantages
• The cost of electricity makes it expensive to use as a heating fuel.
• With space heaters, we can't easily provide central filtration, humidification or cooling.
• The electrical hazard of shock and fire caused by electricity is an issue.
• There are a cost associated with Electric heat requires a larger electrical service than normal.
Essential requirements of good heating element
The materials used for heating element should have the following properties:
• High-specific resistance: Material should have high-specific resistance so that small length of wire may be required to provide given amount of heat.
• High-melting point: It should have high melting point so that it can withstand for high
temperature, a small increase in temperature will not destroy the element.
• Low temperature coefficient of resistance: the radiant heat is proportional to fourth powers of the temperatures; it is very efficient heating at high temperature. For accurate temperature control, the variation of resistance with the operating temperature should be very low. This can be obtained only if the material has low
temperature coefficient of resistance.
• Free from oxidation: The element material should not be oxidized when it is subjected to high temperatures; otherwise the formation of oxidized layers will shorten its life.
• High-mechanical strength: The material should have high-mechanical strength and should withstand for mechanical vibrations.
• Non-corrosive: The element should not corrode when exposed to atmosphere or any other chemical fumes.
• Economical: The cost of material should not be so high.
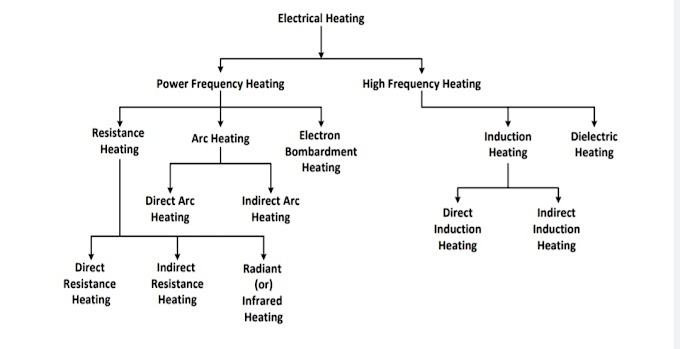
Classification of electric heating method
Electric heating may classified as ;
Electric heating can be broadly classified under two categories:
(a) Power frequency heating in which the furnace operates with 50Hz AC supply.
(b) High frequency heating in which special high frequency generators is essential, e.g. dielectric heating, induction heating.
(A) Power frequency heating
1. Resistance heating
(i) Direct resistance heating
• The electric current is made to pass through the substance to be heated or charge
itself. The electric current while passing through charge products I2R loss which appears in the form of the heat thus charge is heated up.
• Few examples of this heating method are resistance welding, electrode boiler for heating water, salt bath furnace.
(ii) Indirect resistance heating
• Current is passed through heating element and I2R loss is produced which appears
in the form of heat.
• This heat is passed on to the substance or charge to be heated by radiation and convection.
• e.g. room heater, hair drier, soldering iron, immersion water heater, hot plate, frying pan, electric oven etc.
(iii) Radiant or Infrared heating
• Heat energy from an electric lamp is focused on the charge to be heated.
• The heat energy is transferred through electromagnetic radiations.
• This is used for drying the paint on objects.
2. Arc heating
(i) Direct arc heating
• An arc is made to strike between electrodes and charge itself.
• The heat energy of arc is absorbed by the charge and thus heating is done.
(ii) Indirect arc heating
• An arc is made to strike between two electrodes.
• The heat of arc is then passed on to the charge through radiation.
3. Electron bombardment heating
Bombardment of electron causes heating.
(B) High frequency heating
1. Induction heating
In this method, current are induced in the charge by electromagnetic induction action
and circulation of these currents in the charge causes its heating. This is used in metallurgical industries for melting the metals.
(i) Direct induction heating
• Currents are induced in the charge by electromagnetic induction action in case of steel and other metals these currents are sufficient enough to melt the metals.
• The equipment used for melting is known as induction furnace and processes used for general heat treatment of metals is known as eddy current heating.
(ii) Indirect induction heating
• Eddy currents are induced in the heating element by electromagnetic induction, the heat so produced is transferred to the charge by radiation and convection and certain heat treatment methods for metals make use of this method.
2. Dielectric heating
Dielectric loss is produced in the charge itself when it is subjected to alternating electric
field. This dielectric loss appears in the form of heat thus charge is heated up.
Resistance heating
• When current passes through a resistance, Power loss takes place there in which appears in the form of heat,
• Electrical energy converted into heat energy
H = I2Rt
Power loss = I2R Watts
= VI Watts
= V2/R Watts
Where,
R=Resistance of the element (Ω)
V=Voltage (Volt)
I=Current (ampere)
Resistance heating are also divided into two types :
(a) Direct Resistance Heating
(b) Indirect Resistance Heating
(a) Direct Resistance Heating
• In this method, electrodes are immersed in a material or charge to be heated.
• The charge may be in the form of powder, pieces or liquid.
• The electrodes are connected to AC or DC supply.
• In case of DC or 1-Φ AC, two electrodes are immersed and three electrodes are
immersed in the charge and connected to supply in case of availability of 3- Φ supply.
(b) Indirect Resistance Heating
• In this method of heating, electric current is passed through a wire or other high resistance material forming a heating element.
• The heat proportional to I2R loss produced in the heating element is delivered to the charge by one or more of the modes of transfer of heat i.e. convection and radiation.
• An enclosure known as heating chamber is required for heat transfer by radiation and convection for the charge.
• For industrial purposes, where a large amount of charge is to be heated then the heating
element is kept in a cylinder surrounded by jacket containing the charge.
If you want to know about different topics in electrical engineering .you can click the following links mention below :





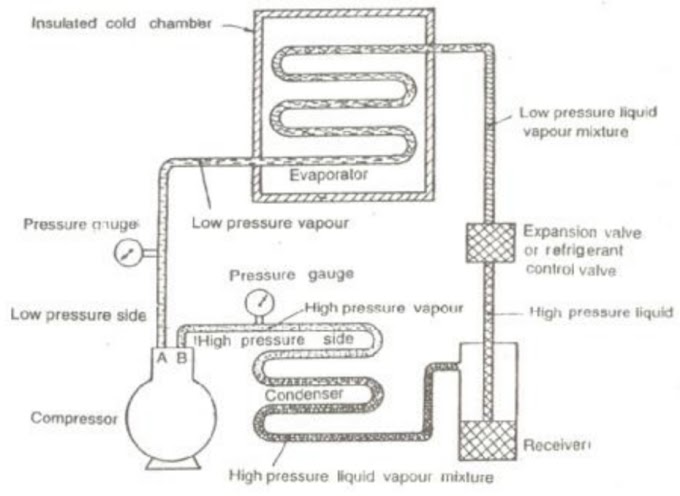








0 Comments